Introduction
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, introduced a novel concept called “mining” as a mechanism to add transactions to its ledger, known as the blockchain. However, unlike traditional mining, Bitcoin mining is a digital process that involves solving complex mathematical problems. This process is deliberately designed to be resource-intensive and difficult, a decision that plays a crucial role in the security and functionality of the Bitcoin network.
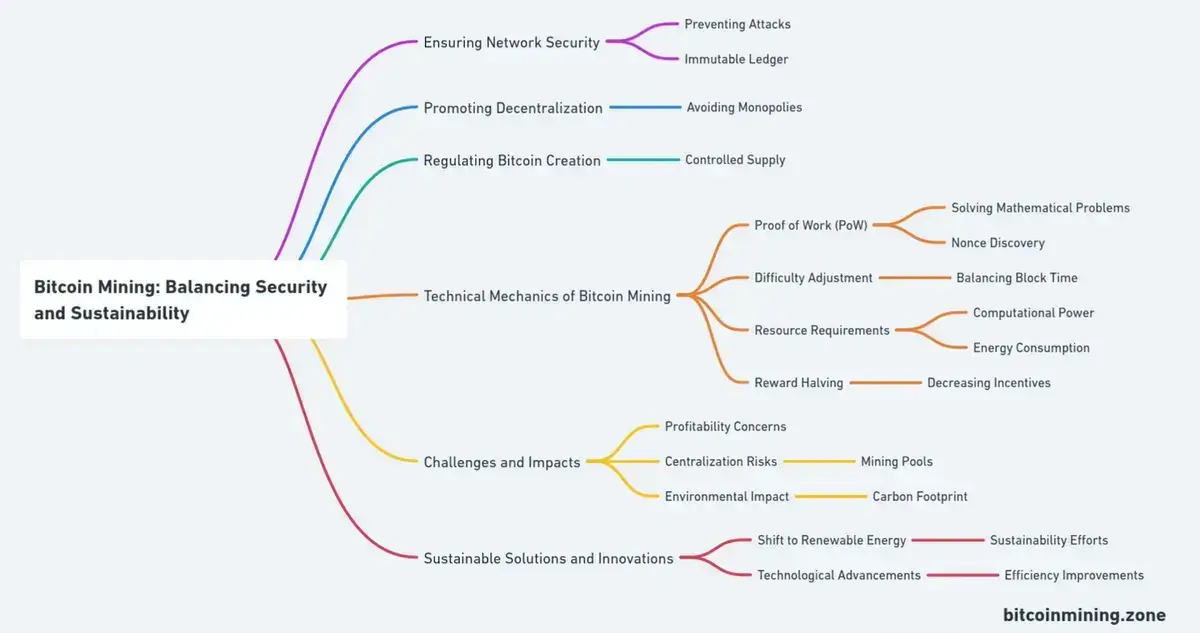
The Purpose of Resource-Intensive Mining
Bitcoin mining, a cornerstone of the cryptocurrency’s framework, serves multiple critical functions beyond mere transaction processing. This process, intentionally designed to be resource-intensive, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the overall health and functionality of the Bitcoin network. The primary objectives of Bitcoin mining can be categorized into three fundamental aspects: ensuring network security, promoting decentralization, and regulating the creation of new bitcoins. Each of these aspects is crucial for maintaining the stability and trustworthiness of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Let’s delve into these aspects to understand how they contribute to the robustness of Bitcoin.
1. Ensuring Network Security
- Preventing Attacks: The high cost of mining acts as a deterrent against attacks. It’s prohibitively expensive for an attacker to gain control of a majority of the network’s hash power.
- Immutable Ledger: The work required to add transactions to the blockchain makes it extremely difficult to alter past transactions, ensuring the integrity of the blockchain.
2. Promoting Decentralization
- Avoiding Monopolies: By requiring significant investment in hardware and energy, Bitcoin aims to prevent any single entity from dominating the mining process, although this has been partially challenged by the emergence of large mining pools.
3. Regulating Bitcoin Creation
- Controlled Supply: The mining process is the only way new bitcoins are created. The difficulty adjustment mechanism ensures that the rate of creation remains steady and predictable.
The Mechanics of Bitcoin Mining
At the heart of Bitcoin mining lies a set of complex technical processes, each playing a critical role in the functioning and security of the Bitcoin network. These processes are not just about creating new bitcoins but are integral to the maintenance and integrity of the blockchain. From the Proof of Work (PoW) protocol that forms the basis of mining to the strategic adjustments and requirements that sustain the network, each element is a cog in the intricate machinery of Bitcoin’s ecosystem. This section delves into the core components of Bitcoin mining: the PoW mechanism, the difficulty adjustment process, the substantial resource requirements, and the system of reward halving. Understanding these elements is key to comprehending how Bitcoin maintains its security, efficiency, and economic viability. Let’s explore these technical aspects to gain a deeper insight into the world of Bitcoin mining.
1. Proof of Work (PoW)
- Solving Mathematical Problems: Miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle, and the first to solve it gets the right to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain.
- Nonce Discovery: The process involves finding a nonce (a random number) that results in a hash below a certain target.
2. Difficulty Adjustment
- Balancing Block Time: The Bitcoin network adjusts the mining difficulty approximately every two weeks to maintain an average block time of 10 minutes.
3. Resource Requirements
- Computational Power: Requires powerful processors, typically Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), designed specifically for Bitcoin mining.
- Energy Consumption: Mining consumes a significant amount of electricity, leading to high operational costs.
4. Reward Halving
- Decreasing Incentives: Approximately every four years, the reward for mining a new block is halved, reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are introduced into circulation.
Economic and Environmental Implications
While Bitcoin mining is an essential component of the cryptocurrency’s ecosystem, it is not without its challenges and broader impacts. These issues range from the economic to the environmental, each presenting unique concerns and considerations for miners, investors, and the global community. In this section, we’ll explore the multifaceted nature of these challenges. Firstly, we’ll examine the profitability concerns that miners face, where the delicate balance between operational costs and mining rewards is constantly in flux. Secondly, we’ll delve into the risks of centralization, a byproduct of the formation of mining pools as a strategy to mitigate high costs. Lastly, we’ll discuss the significant environmental impact of Bitcoin mining, particularly its carbon footprint, which has become a topic of global concern. Understanding these challenges is crucial for anyone involved in or affected by the world of Bitcoin mining.
1. Operational Costs vs. Rewards
- Profitability Concerns: Miners must balance the cost of electricity and hardware against the rewards from mining, which can vary with the price of Bitcoin.
2. Centralization Risks
- Mining Pools: The high costs have led to the formation of mining pools, where miners combine their computational power, potentially leading to centralization.
3. Environmental Impact
- Carbon Footprint: The significant energy consumption of Bitcoin mining has raised concerns about its environmental impact, particularly in regions where electricity is generated from fossil fuels.
Future Trends and Alternatives
In response to the challenges posed by traditional Bitcoin mining practices, the cryptocurrency sector is witnessing a paradigm shift towards more sustainable and efficient alternatives. This shift is not just a response to the environmental and economic challenges but also a proactive step towards a more sustainable future for digital currencies. In this section, we explore three key developments that are shaping the future of cryptocurrency mining. First, we look at the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources within the mining community, a crucial move towards reducing the environmental impact of mining activities. Next, we delve into the emergence of Proof of Stake (PoS) as an alternative mechanism to the traditional Proof of Work (PoW), offering a less energy-intensive way of maintaining blockchain integrity. Finally, we examine the ongoing technological advancements in mining hardware, focusing on efficiency improvements that aim to alleviate environmental concerns. These developments represent a collective effort to balance the demands of cryptocurrency mining with the pressing need for environmental sustainability and energy efficiency.
1. Shift to Renewable Energy
- Sustainability Efforts: There’s a growing trend in the mining community to use renewable energy sources to reduce the environmental impact.
2. Proof of Stake (PoS)
- An Alternative Mechanism: Some newer cryptocurrencies use PoS, which requires validators to hold and stake their coins to participate in the block validation process, consuming far less energy than PoW.
3. Technological Advancements
- Efficiency Improvements: Continuous improvements in mining hardware efficiency could help mitigate some of the environmental concerns.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining’s design as a resource-intensive and challenging process is fundamental to the security and decentralized nature of the network. While this approach has been effective in maintaining a secure and decentralized blockchain, it also presents significant economic and environmental challenges. The future of Bitcoin mining may see a shift towards more sustainable practices and technological innovations, balancing the need for security with environmental responsibility.
FAQ:
1. What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of using computer hardware to perform complex calculations that validate transactions and secure the Bitcoin network. Miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles, and the first to solve it adds a new block to the blockchain.
2. Why is Bitcoin mining deliberately resource-intensive?
Bitcoin mining is designed to be resource-intensive to ensure network security, promote decentralization, and control the rate of new Bitcoin creation. The difficulty of mining prevents easy manipulation of the blockchain.
3. What is Proof of Work (PoW) in Bitcoin mining?
Proof of Work is a consensus mechanism used in Bitcoin mining where miners must solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain.
4. How does the difficulty adjustment work in Bitcoin mining?
The Bitcoin network adjusts the mining difficulty approximately every two weeks to maintain an average block time of 10 minutes, ensuring a steady rate of block creation.
5. What are the main resources required for Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining primarily requires computational power, typically from specialized hardware like ASICs, and a significant amount of electricity.
6. What is reward halving in Bitcoin mining?
Reward halving is an event that occurs approximately every four years, where the reward for mining a new block is halved, reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are introduced into circulation.
7. What are the profitability concerns in Bitcoin mining?
Miners must balance the costs of electricity and hardware against the rewards from mining, which can vary with the price of Bitcoin, affecting profitability.
8. How do mining pools relate to centralization risks in Bitcoin?
Mining pools, where miners combine their computational power, have emerged due to high costs, potentially leading to centralization and challenging Bitcoin’s decentralized nature.
9. What is the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining consumes a significant amount of electricity, leading to a high carbon footprint, especially in regions where electricity is generated from fossil fuels.
10. How is the shift to renewable energy affecting Bitcoin mining?
There’s a growing trend in the mining community to use renewable energy sources to reduce the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining.
11. What is Proof of Stake (PoS), and how does it differ from PoW?
Proof of Stake is an alternative consensus mechanism where validators stake their coins to participate in block validation, consuming far less energy than Proof of Work.
12. What technological advancements are improving Bitcoin mining efficiency?
Continuous improvements in mining hardware efficiency, such as more energy-efficient ASICs, are helping to mitigate some of the environmental concerns associated with Bitcoin mining.
13. How does Bitcoin mining ensure the security of the network?
The high cost and difficulty of mining act as deterrents against attacks, making it economically unfeasible for attackers to control a majority of the network’s hash power.
14. Why is the Bitcoin ledger considered immutable?
The work required to add transactions to the blockchain makes it extremely difficult to alter past transactions, ensuring the integrity and immutability of the blockchain.
15. How does Bitcoin mining contribute to decentralization?
By requiring significant investment in hardware and energy, Bitcoin mining aims to prevent any single entity from dominating the process, promoting a decentralized network structure.

