Cryptocurrency has captivated the imagination of the digital world, and at the heart of this fascination lies Bitcoin, the first decentralized currency. To understand the network’s backbone, it’s essential to delve into the concept of Bitcoin mining pools, which play a significant role in the cryptocurrency’s ecosystem. In this article, we will explore what mining pools are, their advantages and disadvantages, identify some of the main pools, and analyze their performance over the last 30 days.
What is a Bitcoin Mining Pool?
To appreciate the role of Bitcoin mining pools, one must first understand the process they are a part of: Bitcoin mining. Mining is the engine that powers the Bitcoin network. It is the process by which transactions are verified and added to the public ledger, known as the blockchain. Moreover, mining is how new Bitcoin is brought into circulation. The process is metaphorically referred to as ‘mining’ because it involves a considerable amount of computational work, much like physical mining involves labor to extract valuable minerals.
In the early days of Bitcoin, mining was feasible on regular desktop computers. Miners were individuals who used their hardware to process transactions and were rewarded with new Bitcoin. However, as Bitcoin gained popularity, the difficulty of the network’s algorithms increased exponentially. This evolution meant that the computational power required to mine effectively also increased. Mining became less viable for individuals due to the high cost of the required electricity and specialized hardware.
As a result, miners began to pool their resources together. Mining pools emerged in late 2010 to address the growing difficulty of the mining process. These pools allowed individual miners to contribute to the overall effort of mining, with each participant’s chance of earning a reward increasing in proportion to the computing power they provided. Instead of facing the volatility of solo mining, where rewards could be infrequent and unpredictable, miners could now receive smaller, but more regular payouts from the pool’s earnings.
The concept is similar to entering a lottery syndicate, where players pool their money to buy tickets, and if any ticket wins, the prize is shared in proportion to each player’s contribution. In a Bitcoin mining pool, if one participant’s hardware contributes to the completion of a new block, the reward, in the form of newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees, is distributed among all participants of the pool.
The formation of mining pools has been a significant development in the Bitcoin ecosystem. They have democratized mining, enabling individuals to continue participating profitably despite the increasing industrialization of Bitcoin mining. However, mining pools are also a double-edged sword; they centralize the process to some extent. This centralization is somewhat antithetical to the original vision of a decentralized Bitcoin network where no single entity would have too much control.
Over the years, the balance of power has shifted within the mining community. Today’s mining pools are sophisticated operations that offer a variety of services and technologies to their members. They have sophisticated methods for managing the distribution of rewards, ensuring security, and optimizing the mining process. Mining pools are now a critical part of the Bitcoin network’s infrastructure, enabling it to run smoothly and efficiently while providing individual miners with the chance to be a part of the mining community. However, with their growth and influence, they carry the responsibility of maintaining the decentralization that makes Bitcoin unique.
Bitcoin mining pools are the collaborative heartbeat of the Bitcoin mining process, allowing individuals to combine their computational power for greater efficiency and more consistent mining rewards. This innovation has ensured the inclusivity of the mining process but has also introduced complexities that the community continues to navigate.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin Mining Pools
Pros:
- Increased Consistency: Pools provide miners with more regular payouts compared to individual mining.
- Collective Power: By pooling resources, miners can combine their computational power to compete more effectively.
- Reduced Risk: The collaborative effort reduces the risk of the high variance and unpredictability associated with solo mining.
Cons:
- Centralization Risks: Large pools could potentially control a significant portion of the network’s hash rate, leading to centralization, which is contrary to Bitcoin’s decentralized ethos.
- Fees: Mining pools typically charge fees, which can reduce miners’ overall profits.
- Trust: Miners must trust the pool operators to distribute rewards fairly and not to engage in dishonest practices.
List of Main Bitcoin Mining Pools Below is a list of some of the prominent Bitcoin mining pools, along with their web addresses, known for their reliability and service to the community:
- AntPool – https://antpool.com
- Foundry USA – https://foundryusa.com
- ViaBTC – https://viabtc.com
- F2Pool – https://www.f2pool.com
- Binance Pool – https://pool.binance.com
(Disclaimer: URLs are for informational purposes only. Exercise due diligence before participating in any mining activity.)
The State of Bitcoin Mining Pools: An Analysis Over the Last 30 Days
Over the past month, the mining landscape has shown interesting trends. The data indicates that AntPool and Foundry USA have been leading in revenue generation, together accounting for over 55% of the total revenue among pools. This raises questions about the potential for centralization, as these two entities hold a significant portion of the mining power.
However, it’s not all about the top players. The ecosystem also features a variety of smaller pools, contributing to the diversity and decentralization of the mining process. Pools like ViaBTC, F2Pool, and Binance Pool also play a critical role in the ecosystem.
The following data from the last 30 days offers insight into the revenue breakdown of mining pools:
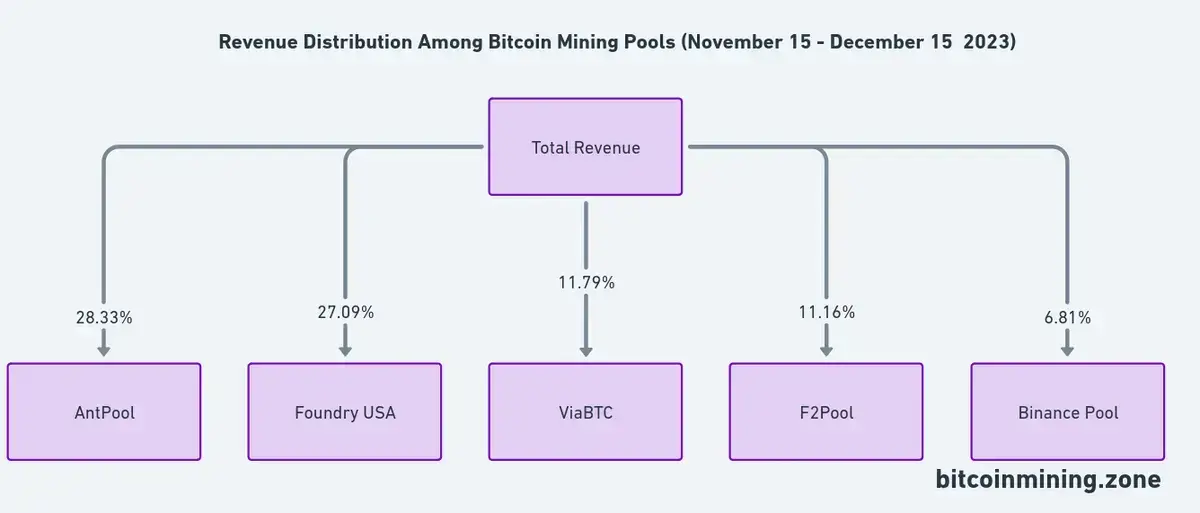
Other smaller pools contribute to the remaining percentage, with no single pool dominating this segment. This distribution suggests a relatively healthy competition among the smaller players, which is vital for the decentralization of Bitcoin’s mining power.
Conclusion
Understanding Bitcoin mining pools is fundamental for anyone interested in the cryptocurrency space. While the concept of pooling resources offers numerous benefits to individual miners, it also introduces potential risks that need to be managed. The recent data reveals a competitive but concentrated mining pool landscape, reminding us of the constant balance between cooperation and the foundational principle of decentralization in Bitcoin. As a beginner or enthusiast, staying informed and vigilant about these dynamics is key to participating wisely in the world of cryptocurrency mining.
FAQ:
1. What is a Bitcoin mining pool?
A Bitcoin mining pool is a group of miners who combine their computational resources to increase their chances of solving the mathematical puzzles required to validate transactions and earn Bitcoin rewards.
2. Why do miners join a pool?
Miners join pools to increase their likelihood of earning rewards. Instead of mining on their own and facing stiff competition, they contribute to a collective effort, which offers more frequent but smaller rewards.
3. How are rewards distributed in a mining pool?
Rewards are typically distributed based on the amount of computational power each miner contributes to the pool, which is often measured in shares.
4. What are the fees for joining a mining pool?
Most mining pools charge a fee, which can range from 1% to 3% of the miner’s earnings, to cover the costs of running the pool’s servers and other expenses.
5. What is a ‘share’ in Bitcoin mining?
A ‘share’ is a unit that mining pools use to measure the work performed by a miner. It represents a miner’s contribution to the pool’s chances of finding a block.
6. Can I mine Bitcoin on my own without joining a pool?
Yes, you can mine Bitcoin independently, but the chances of solving a block on your own are very slim due to the high level of competition and the significant computational power required.
7. Are all mining pools the same?
No, mining pools vary in size, payout structure, fees, and other features. Miners should choose a pool that fits their needs and preferences.
8. What is a ‘hash rate’?
The hash rate is a measure of the computational power per second used in mining. It’s an indicator of how many attempts a miner can make to solve a block in a given timeframe.
9. Is it profitable to join a Bitcoin mining pool?
Profitability depends on several factors, including the cost of electricity, the efficiency of your mining hardware, and the current price of Bitcoin.
10. How do I choose a mining pool?
Consider the pool’s size, fee structure, payout frequency, minimum payout, reputation, and the user interface when choosing a mining pool.
11. What is a 51% attack?
A 51% attack occurs when a miner or group of miners controls more than 50% of the network’s mining power, which could potentially allow them to disrupt the network by double-spending coins and preventing new transactions from confirming.
12. How do mining pools prevent fraud?
Mining pools implement various security measures, including regular audits, transparent reward distribution systems, and proof-of-work validation to prevent fraud and ensure fair distribution of rewards.
13. Can a mining pool guarantee steady income?
While mining pools can provide more regular payouts, they cannot guarantee a steady income as Bitcoin’s price and mining difficulty fluctuate.
14. What happens if a mining pool closes down?
If a mining pool closes, miners will not receive payouts from that pool anymore and will need to join another pool to continue mining.
15. Are Bitcoin mining pools legal?
Bitcoin mining and participation in mining pools are legal in most countries. However, it’s important to check local regulations as the legal status can vary.

